
What does data protection mean?
Basics of data protection
Basics of data protection

This so-called "personal data," i.e., information that makes a person directly or indirectly identifiable, includes, for example, data such as full name, date of birth, address or telephone number. Particularly sensitive personal data (e.g., health, origin, political orientation, religion, etc.) belong to the special categories of personal data and are thus given special protection.
In Germany, the legal basis for data protection is provided by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Federal Data Protection Act (BDSG), among others.
By the way: The EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) does not only apply in the EU, but to everyone who processes data of EU citizens. A significant difference!
Data is no longer considered personal if it has been anonymized in a way that data subjects can no longer be identified. For example, information in elections or surveys is anonymized so that it's impossible to identify a certain participant. Likewise, collective e-mail addresses of a company with the format info@company.com, for example, are not personal. The statistics and marketing data used by companies for planning, research and market analyses are also no longer personal once they have been anonymized.
| Data | Personal | Not personal |
|---|---|---|
| Full name | ||
| Contact data | ||
| Adress | ||
| Bank data | ||
| Biometric data | ||
| Origin | ||
| Sexual orientation | ||
| Health data | ||
| Religion | ||
| Political views | ||
| Trade union membership | ||
| Collective company email address | ||
| Anonymised survey data |
In practical terms, this means that the collection, storage and processing of personal data is basically prohibited by default, unless:
We have a modern and comprehensive data protection training that will effectively train your employees on how data protection works.
Personal data is processed according to seven principles that are mandatory for every company or organisation:
Every person whose personal data is collected and processed has the following rights:
As global digitalization continues to spread, the need to better protect data and personal information is steadily increasing. Because with digitalization, the criminal misuse of data has also increased.
This is also recognized by politicians with the implementation of laws such as the European Data Protection Regulation ('EU GDPR') or the German Federal Data Protection Act ('BDSG'). Thus, the goal is: everyone should be able to determine for themselves who collects, stores and processes their personal data, when and for what purpose.
In order to sensitize your employees on how data protection works, we offer an easy-to-understand data protection training.
Data protection is important. Therefore, as a company, you can't really avoid regular and often unpopular employee awareness training. For you to fulfill your training obligation without overburdening your employees, we have thought out an exceptional data protection training that:

Up-to-date and modern online data protection training courses make your employees fit for GDPR. Find out more and book training now!

Modern and entertaining IT security trainings protect your company from attacks and their consequences.

How to repackage familiar GDPR content into exciting online courses.

Find out how companies can properly motivate their employees to complete an e-learning course on cyber security, data protection or compliance.
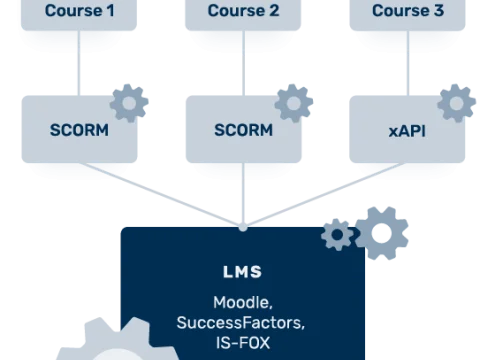
In this article, we explain the technical terms Scorm, LMS and e-learning course.
Technical settings and tips for LMS administrators