
The General Equal Treatment Act (AGG) at a glance: What employers need to know.
Discrimination is never an option - neither in the workplace nor outside it. The AGG ensures this.
Discrimination is never an option - neither in the workplace nor outside it. The AGG ensures this.

The General Equal Treatment Act is also commonly known as the Anti-Discrimination Act. It prohibits discrimination on the basis of these protected characteristics:
The Equal Treatment Act is a German federal law designed to prevent and eliminate discrimination against individuals. Discrimination means that a person is treated less favorably than another person by a private actor without objective reason and because of (one of) the above-mentioned characteristics. Private actors are, for example, employers, landlords and providers of goods and services.
The General Equal Treatment Act also protects all people equally in their working environment. Regardless of whether they have a permanent employment contract, are in training or studying, working on a freelance basis or are just applying for a job. Unequal treatment and discrimination are a no-go in all areas of the professional environment - from job interviews to employment contracts, from performance appraisals to promotions or further training.
Here are a few specific examples of discrimination in working life:

These examples are very clearly discriminatory. However, there are also less obvious cases that nevertheless violate equal treatment.
A person is discriminated against on the basis of protected characteristics such as gender, origin, religion, disability or sexual orientation.
Example: An employer does not hire a qualified female applicant because they believe that women are unsuitable for the position in question.
A regulation or practice that appears to be neutral actually discriminates against certain groups of people with protected characteristics.
Example: A job description requires perfect German language skills for driving a vehicle, although perfect German language skills are not required for this. This automatically puts foreign applicants at a disadvantage.
This refers to behavior that violates a person's dignity or creates a hostile environment. This includes hostility, humiliation or insults.
Example: This specifically includes sexual harassment such as vulgar remarks, groping or hanging up lewd pictures.
Someone is instructed to carry out or participate in a discriminatory act.
Example: A manager tells their employees not to serve customers of a certain religion.
A person is discriminated against or harassed for exercising or supporting their rights under the Equal Treatment Act.
Example: An employee is dismissed after making a complaint of sexual harassment in the workplace.
Employers are obliged to publicize the AGG within the company and take preventative measures against discrimination. How exactly the AGG is communicated is up to the employer, as long as the communication is accessible and understandable for everyone.
In addition to an intranet, regular training courses, e.g. our compliance training, are particularly suitable for informing employees about the AGG and sensitizing them to the topic of (anti-)discrimination.
Employers are also obliged to set up a complaints office for employees. It is also important that every complaint must be investigated and that the reporting person must not suffer any disadvantages. This is because all employees should feel safe to report incidents of discrimination without fear of retaliation.
Employers should ensure that objective criteria and no discriminatory factors play a role in personnel decisions, such as hiring, promotions or dismissals. Transparent selection procedures with objective criteria that are comprehensible at all times and regularly reviewed are a helpful tool. It is also useful in this context to clearly document personnel decisions so that, in case of doubt, it is clear why certain decisions were made.
Companies can also take measures to promote diversity within the workforce and ensure that all employees have equal opportunities. This can be achieved, for example, by promoting diversity in management positions and creating flexible working conditions for different needs (e.g. for mothers and fathers, people with disabilities or older people).
It is advisable to conduct regular internal reviews to identify and address potential discrimination risks. By evaluating complaints, feedback from employees and a review of working practices, possible cases of discrimination can be identified at an early stage and countermeasures can be taken.
Equal treatment is often a sensitive issue. Nobody wants to be treated as inferior, because of their person, origin or world view. However, some people may also find it difficult to address the issue at all or find someone they can confide in.
In our opinion, it's all the more important to implement a functioning compliance structure and complaints office. Someone who has experienced discrimination may be more likely to turn to the HR department than to their own boss. If this person would rather turn to a colleague, it is important that their colleagues also know what to do.
Our compliance training was developed by experts and explains the topic of AGG and equal treatment in a way that's easy to understand and implement.
Equal treatment and anti-discrimination is a win-win-win situation for everyone involved:
Get a free demo account now and let's talk about your individual needs in a web meeting. We'll show you how to successfully strengthen compliance in your company through employee training.
Other topics that might interest you

The German "Supply Chain Act" explained in a simple and comprehensive way.

What is a cartel?

Export control is essential for compliance in international trade and regulates the export of goods & technologies.

Corruption & fraud – small "favors" can quickly become crimes.

Explained in a simple and comprehensive way.

Everything important about whistleblowing in a 9-minute learning nugget.

Find out how companies can properly motivate their employees to complete an e-learning course on cyber security, data protection or compliance.

How to repackage familiar GDPR content into exciting online courses.
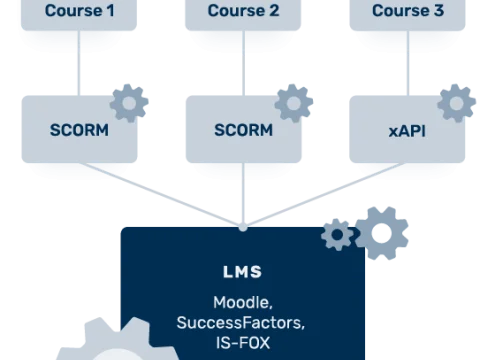
In this article, we explain the technical terms Scorm, LMS and e-learning course.
Technical settings and tips for LMS administrators